Safeguarding accounts payable data is critical to protecting any organization's financial health and reputation.
Imagine the Accounts Payable (AP) department as the guardian to your organization's financial well-being. They manage the flow of money in and out; however, their responsibilities extend far beyond just financial transactions. They are also tasked with safeguarding sensitive data, including both their own financial records as well as critical supplier and vendor information. This dual role makes them an enticing target for increasingly sophisticated cyber-attacks.
Why Should I Care About Financial Data Security?
In today's world of rapid digital transformation, leaving AP data unsecured is equivalent to leaving the vault door ajar with a welcome sign. Organizations must recognize the risks involved and take proactive steps to safeguard sensitive company information. Here are 6 reasons why:
- Compliance Requirements (do it because you must)
Regulatory bodies impose strict deadlines for handing financial data. Non-compliance with these guidelines can result in hefty fines and damage to a company's reputation. - Business Continuity (so you don't disappear)
Streamlined accounts payable processes are critical for efficient business operations. Any breach or interruption can lead to processing and payment delays, affecting cash flow and supplier relationships. - Safeguarding Proprietary Information (only share what you want)
Accounts payable invoices often include sensitive details about suppliers, contracts, and pricing. Protecting this information prevent businesses from losing and competitors from gaining any kind of advantage. - Mitigating Risks (less problems to deal with)
Cyber threats, fraud, and data breaches pose significant risks. Implementing data security measures reduces vulnerability and prevent financial losses. - Maintaining Trust (keep customer confidence strong)
Suppliers, customers, employees, and investors all trust organizations to handle their financial transactions securely. Breaches erode trust and can have long-lasting financial and legal consequences. - Cost Implications of Inadequate Security (don't throw money away)
Recovering from security incidents are expensive. Proactively investing in strong AP data security upfront is more cost-effective than dealing with recovery.

Understanding the Risks
As stated earlier, the stakes for securing sensitive information in the AP department are incredibly high. To effectively guard against potential internal and external threats, it's important to understand the various risks and their possible impact. Here are some of the most common risks that specifically affect AP departments:
Phishing
Phishing attacks involve fraudulent emails or messages that are designed to trick the recipient into revealing sensitive information or downloading malicious software.
Data Breaches
Data breaches can occur through hacking, malware, or even physical theft. These breaches expose confidential information, potentially leading to financial losses and legal liabilities.
Invoice Fraud/Payment Fraud
Invoice fraud happens when attackers manipulate or create fake invoices to siphon funds from an organization.
Ransomware
Ransomware attacks encrypt an organization's data and demand payment for its release. These attacks can potentially cripple financial operations and result in significant financial losses.
Insider Threats
Insider threats can stem from many sources, including disgruntled employees or careless customer data handling.
Unsecured Networks and Systems
Using unsecured networks or outdated systems can leave any organization vulnerable to attacks.
Best Practices to Boost Accounts Payable Security
As technology advances, cyber threats become more sophisticated. This makes ongoing vigilance, advanced security measures and continuous fraud prevention efforts essential. Here are some best practices involving accounting and technology to enhance AP security:
- Password Management: Implement strong password policies, regular updates, and complex password requirements. Use password managers and multi-factor authentication for additional security.
- Data Encryption: Encrypt sensitive data while it is in transit and at rest using Advanced Encryption Standards (AES). This will help protect financial information and personal data.
- Vendor and Supplier Vetting: Thoroughly vet both vendors and suppliers by conducting background checks, verifying credentials, and assessing their security measures to ensure that they meet your organization's security standards.
- Invoice Verification: Implement multi-layered invoice verification processes, cross-checking invoices against purchase orders and delivery receipts, and using automated tools to quickly flag any discrepancies.
- Closed-Loop versus Open-Loop Business Payments Networks: A closed-loop payments network restricts transactions to a predefined group of participants, providing an increased level of security as all parties are already known and vetted.
In contrast, an open-loop payments network allows transactions with a broader range of participants. This offers greater flexibility but also poses higher security risks due to the increased number of unknown entities involved. - Compliance with International Regulations and Laws: Ensure compliance with international data protection regulations and laws that set standards for how personal data should be collected, processed, and stored to ensure privacy and security. Examples include:
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)GDPR compliance is enforced in 30 countries, including the 27 members of the European Union (EU) and the 3 European Economic Area (EEA) countries. It is also required of businesses outside of these countries if they handle any personal data of individuals within this region.
Data Protection Act 2018 (DPA)
UK legislation that complements the GDPR, providing a framework for data protection in the UK including outlining individual rights and organizational responsibilities.
Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX)
A U.S. law designed to protect investors by improving the accuracy and reliability of corporate disclosures. While it focuses on corporate governance, financial reporting, and accountability it also has provisions related to the retention and protection of financial records.
- Staying Current with Emerging Technologies and Solutions: Stay updated on emerging technologies, including AI-powered fraud detection systems, the use of blockchain for conducting secure transactions, and advanced analytics software for monitoring and identifying suspicious activities.
Additional measures to strengthen accounts payable data security include:
- Employee Training: Ensure that employees - particularly AP personnel - are trained to identify and report fraud attempts and scams.
- Regular Audits: Conduct regular security audits and encryption reviews.
- Regular Backups: Implement regular backups and use anti-ransomware software solutions.
- Invoice Fraud Prevention: Use secure invoicing systems with multi-layered verification processes.
- Access Controls: enforce strict access controls including the use of secure networks. Monitor activities to detect and prevent any harmful internal actions.
- System Updates: Keep all networks and systems up to date with the latest security patches. Using cloud-based platforms and software can streamline this process.
By implementing these best practices, organizations and AP departments can significantly reduce the risk of data breaches, safeguard sensitive information, maintain compliance with industry regulations, and protest the organization's reputation and financial health.
The Increasing Risk of Social Engineering
Social engineering, the manipulation of human behavior to gain unauthorized access to sensitive financial information, is an increasing risk for accounts payable data security. Since this tactic relies on exploiting human psychology rather than the more traditional, technical hacking techniques, it is a significant threat for accounts payable processes data security and can result in fraud and financial loss.
Here are some of the most common tactics used in social engineering:
Phishing
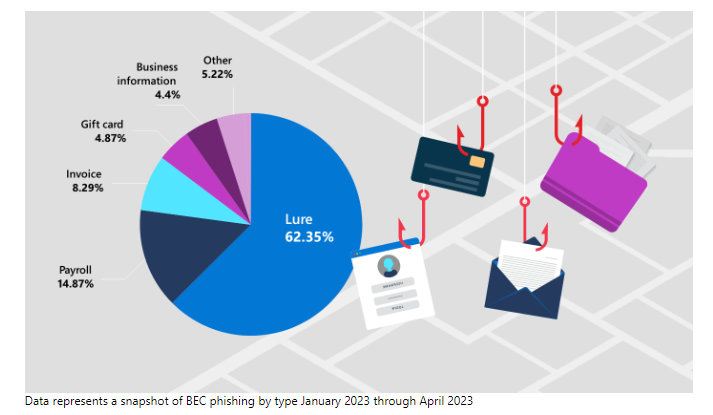
Cybercriminals will pose as trusted vendors or internal personnel and create convincing emails or messages. These fraudulent communications trick staff into revealing confidential information or approving unauthorized transactions. In fact, business email fraud is so effective that the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) reported over 21,000 complaints with adjusted losses over $2.7 billion.
Pretexting
Scam artists create a fabricated scenario to extract information or get access to a system. They come up with a story - the pretext or false excuse - to fool their target. They key is to make the victim believe that the attacker is really the person they are portraying, such as a friendly customer service representative might ask for bank details to fix a payment processing error.
The rise in pretexting attacks - 170 data breaches in 2024 compared to 61 in 2017 - can be attributed to poor security policies and an increase in remote work during and after the COVID pandemic.
Tailgating 
Tailgating, mostly known in terms of driving too close behind another vehicle, in this context simply involves following someone through a locked door. They are often dressed as another employee, repairman, or delivery person.
Social engineers exploit human trust, curiosity, and a sense of urgency, making their attacks particularly effective. Since the victims believe that the attacker is legitimate, they willingly share sensitive data or grant access.
Best Practices for Preventing Social Engineering Attacks
Three best practices for preventing social engineers from succeeding include:
- Regular phishing simulations
- Clear communication channels to report any suspicious activity
- Ongoing education about tactics used by attackers.
Creating a Culture of Security
Fostering a culture of security in accounts payable involves constant vigilance and taking a proactive approach where threats are anticipated, and companies mitigate risk before it even arises. Employee training and awareness are crucial to ensure that everyone understands their role in maintaining security and can recognize potential threats.
To cultivate a security-focused culture, organizations should integrate security into their core values, establish clear policies, and encourage communication about security issues. Leadership plays a pivotal role by prioritizing security initiatives, allocating resources, and setting an example for employees by their own actions.
Leveraging AI to Mitigate Risk
AP software and Artificial Intelligence (AI) in particular are transforming the ap process by significantly enhancing data security. By automating and analyzing large volumes of transactions, AI systems can identify and mitigate potential risks more efficiently and effectively with more control, than traditional, manual methods. This advanced technology ensures that sensitive financial data is protected from unauthorized access and cyber threats. Examples include:
- Machine Learning (ML) Algorithms: Analyze patterns in transaction data, identifying and flagging any suspicious activities and irregularities that may indicate fraudulent behavior. Furthermore, these systems continuously learn from new data, improving their accuracy and effectiveness over time.
- AI Risk Assessment: Evaluates vendor behaviors and payment histories, providing real-time insights to prevent potential issues before they escalate.
- AI-Driven Predictive Analytics: Enables companies to foresee and reduce risks with greater accuracy.
As AI continues to evolve, its role in safeguarding AP data will expand, providing even greater protection against emerging and evolving threats.
Conclusion
Safeguarding accounts payable data is critical to protecting any organization's financial health and reputation. Alongside the rapid advancements in technology, the evolving nature of cyber threats requiring continuous vigilance, agility, and a comprehensive approach towards accounts payable security.
By implementing strong security measures and staying informed about the latest threats, companies can significantly reduce their risk exposure and improve operational efficiency. Act now; review and improve your AP security to ensure the safety of your sensitive financial information.
Ready to see how AP automation software can help secure your data and safeguard your future? Request a personal demonstration today!
FAQs
Why is securing Accounts Payable (AP) data crucial for business operations?
Can hackers really break into our AP system through social engineering?
What is the most famous cyberattack?
Is accounts payable data security limited to companies?
How can accounts payable automation software help ensure accounts payable data security?