Automation is transforming every aspect of business operations. From boosting operational efficiency to elevating both customer loyalty and customer satisfaction, business are embracing digitalization and reaping the benefits of retail automation solutions.
The global retail market is experiencing rapid growth, leaving businesses facing a delicate balancing act between tradition and innovation. As both customer preferences and customer expectations further evolve and e-commerce continues its relentless expansion, the pressure on retailers has never been greater. Margins are tight, costs are rising, and competition is fiercer than ever before.

In such a business climate, digitalization emerges as a powerful transformative force, offering a pathway to an enhanced customer experience, efficiency, agility, and resilience. One critical aspect of this transformation in particular is Accounts Payable (AP) automation, which promises to reshape the way that retail organizations operate.
Let's explore how retail Accounts Payable automation will help businesses streamline their operations, gain better data insights, and make real-time strategic decisions.
The Retail Market is Growing
First, let's examine the scale of the retail market.
The global retail automation market size was valued at approximately $12.2 billion in 2021. According to estimates provided by Next Move Strategy Consulting, experts predict a substantial growth in this market, forecasting it to reach approximately $33.02 billion by 2030.
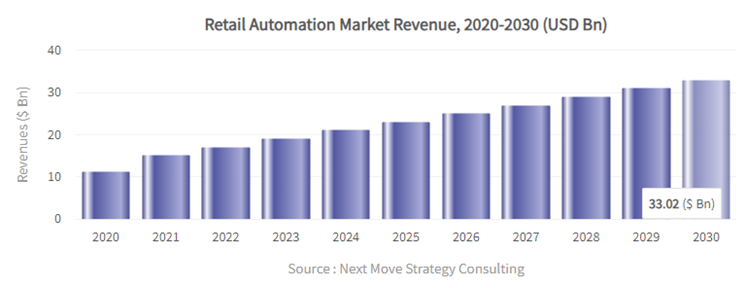
Estimates provided by Next Move Strategy Consulting
What is Retail Automation?
Automation in general is a powerful tool embraced by companies wanting to streamline processes, increase productivity, and reduce costs. Retail automation refers to retailers using automated retail technologies to optimize processes and drive operational efficiency with minimal human intervention.
The pace of this transformation is staggering. According to the World Economic Forum, the retail sector is already 40% automated and this figure could grow to 60-65% within the next three to four years.
Common Forms of Retail Automation
Here are some of the most common forms of retail automation:
Chatbots
Retailers use chatbots to automate and enhance customer service tasks like answering common questions and handling returns and refunds. Examples include promptly responding to frequently asked questions or initiating return requests or refunds.

Chatbots offer 24/7 availability, provide consistent responses, and can handle multiple inquiries at the same time.
Self-Checkout Systems
These systems help customers to expedite the checkout process, allowing them to scan and pay for their purchases in person or online orders without the assistance of a cashier. This results in fast transactions and reduce waiting times and results in reduced labor costs since retailers can then allocate staff towards other work.
Automated Warehouses
Robots and advanced technologies automate order fulfillment processes like picking and packing orders, reducing errors, and boosting efficiency. Using robots is typically faster and more accurate and because fewer humans are needed for these repetitive manual tasks, automated warehouses result in reduced labor costs.
Automated Inventory Management
The purpose of automating inventory management is to improve efficiency in managing stock levels and reordering products. Inventory management software offers automatic real-time inventory data, the ability to generate Purchase Orders (PO) if the stock falls below a certain level, and even reorder the products.
products. Inventory management software offers automatic real-time inventory data, the ability to generate Purchase Orders (PO) if the stock falls below a certain level, and even reorder the products.
While you've probably already encountered using chatbots and self-checkout systems, it's the latter ones - the use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) combined with financial automation - where the difference rapidly becomes clear.
7 Compelling Benefits That You Don't Want to Miss
The adoption of automation in retail has had a significant impact on the industry, serving as a key component of digital transformation and transforming the way that retailers operate.
By seamlessly integrating technology into everyday operations like inventory management, ordering, and payments - all previously performed by humans - automation in retail provides a host of benefits that reduce costs, enhance the customer experience, and improve overall retail business' performance.
Here are seven of the key benefits that automation brings to the retail industry:
1. Increased efficiency
 Automation helps retailers to perform routine tasks faster and more accurately, allowing retailers to operate more efficiently. Tedious processes such as inventory management, order processing, and payment handling are automated, which frees up valuable time for employees to focus on other tasks.
Automation helps retailers to perform routine tasks faster and more accurately, allowing retailers to operate more efficiently. Tedious processes such as inventory management, order processing, and payment handling are automated, which frees up valuable time for employees to focus on other tasks.
In addition, automation ensure accessibility 24/7, from any location.
Furthermore, multi-location retailers benefit from centralized data storage. Everybody is working with the same information, improving consistency and efficiency.
2. Reduced Operating Costs
No more tedious, error-prone, and labor-intensive manual activities! Automation reduces operational costs associated with labor, paperwork, mail, and physical storage.
By minimizing reliance on time-constrained human intervention, retailers can allocate resources more strategically for a leaner, agile operation.
3. Greater Accuracy
Hand-in-hand with a reduction in manual labor is a reduction in human error. Automated systems quickly process data, including double-checking and triple-verifying critical information. This improves accuracy in inventory management and accounts payable processing.
4. Increased Security 
Automation serves as a safeguard against both internal and external fraud.
My reducing manual intervention, retailers not only improve accuracy but reduce the possibility of errors that could compromise security.
5. Improved Customer and Supplier Experience
Thanks to automation tools, retailers can provide faster, more convenient service to both customers and suppliers. From tracking an order or resolving issues, experiencing reduced waiting times, real-time access to information, and seamless interactions create a positive experience for all parties.
6. Real-Time Insights
Retail operations depend upon data. Automation collects and analyzes information in real-time, providing actionable insights. Retailers can easily monitor rends, identify opportunities, and make informed decisions promptly.

7. Employee Satisfaction
One in four workers left their job this year, making employee satisfaction and retention an increasing priority for retailers. Automation helps to reduce mundane activities and allow for increased employee interaction and challenge.

Challenges of Automation Technologies in Retail
In navigating the shift towards digitalization, the retail industry faces several potential challenges including:
1. Operational Complexity
Retail operations involve a wide range of responsibilities, from overseeing inventory and vendors to ensuring quality customer service and maximizing sales. Timely payment and recording of invoices, continuous training and monitoring of hourly employees, and precise forecasting are all crucial to stay within budgetary confines.
The challenge increases when managing all of the above for multiple locations.
To handle this complexity effectively, advanced technological solutions such as Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems or specialied Accounts Payalbe (AP) automation software are indispensable. They help navigate through the various retail operations, streamlining processes and providing comprehensive oversight across various locations.
2. Diverse Stakeholder Needs
 Retail customers, suppliers, and vendors possess diverse needs, making them challenging to predict. Furthermore, retailers must strike a balance between providing a customized experience and leveraging automation to improve efficiency.
Retail customers, suppliers, and vendors possess diverse needs, making them challenging to predict. Furthermore, retailers must strike a balance between providing a customized experience and leveraging automation to improve efficiency.
One effective solution involves communicating the advantages of automation, highlighting its role in supporting rather than impeding the overall journey. This approach helps cultivate buy-in, reduce opposition, and foster ongoing support for digitalization.
3. Evolving Technology
The relentless pace of technological advancements poses an ongoing challenge for the retail industry. It is important to stay abreast of the latest innovations in retail automation software, whether on-site solutions such as self-checkout or cloud-based services such as AP automation.
Partnering with cloud-based providers can alleviate the need to stay current with technology trends including the most advanced security.
4. Cost
 Implementing automation often requires significant initial investment, including technology investments, infrastructure upgrades, and ongoing employee training. This potential financial burden can be especially discouraging for small retailers who typically operate on tight margins, presenting a particularly daunting financial hurdle to overcome.
Implementing automation often requires significant initial investment, including technology investments, infrastructure upgrades, and ongoing employee training. This potential financial burden can be especially discouraging for small retailers who typically operate on tight margins, presenting a particularly daunting financial hurdle to overcome.
Fortunately, the nature of Software-As-A-Service (SaaS) is a promising solution, offering a more accessible way for businesses of all sizes to embrace automation and stay competitive in the marketplace.
5. Resistance to Change
Overlooking the human factor can undermine automation efforts. More traditional employees and customers may be apprehensive about the new technology, viewing automation as a threat to job security.
Proactive measures such as transparent communication, comprehensive training initiatives, and being sure to highlight the benefits of automation as a support - not replacement - for human roles are all essential measures for a smooth transition.

Summary
As technology evolves, the choice of whether to adopt automation emerges as a pivotal choice for the retail industry. Those who embrace this transformative technology stand to thrive, while those who resist risk falling behind.
The use of automation technology in the retail industry will continue to reshape the shopping experience. Thanks to the integration of advanced technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI) and robotics, retailers can streamline their operations, cultivate stronger vendor partnerships, and access real-time data insights to craft personalized customer experiences.
However, as automation continues to grow, it's important to acknowledge and address any challenges which it may pose, particularly the impact on the workforce.
One thing is clear: the potential for automation in retail is endless. The silver lining? Nobody has to do it alone!
Yooz Can Help
The Yooz automation solution transforms retail operations, streamlining Accounts Payable (AP) operations to alleviate the burden of manual tasks and increase invoice process efficiency. Both flexible and scalable, Yooz helps retail businesses to swiftly respond to dynamic market conditions and evolving customer preferences.
Reach out today for a personalized demonstration on what Yooz can do for you!
Automation in Retail FAQs
What does intelligent automation mean for the retail industry?
Intelligent automation in retail refers to the integration of advanced technologies like AI and robotics to streamline operations, boost efficiency, and drive innovation.
How does retail automation enhance the customer experience?
Retail automation enhances the customer experience by helping to provide faster service, access to real-time information, and creating a seamless interaction experience. Together these ultimately improve satisfaction and loyalty.
How does Accounts Payable (AP) automation benefit retail businesses?
Benefits to retail include streamlining invoice processing, reducing manual errors, improving cash flow management, and providing better insights for strategic decision-making. These all contribute to creating an elevated customer experience, including greater customer loyalty and satisfaction.
What are some challenges retailers face when implementing automation techniques?
Some of the challenges that retailers face when implementing automation techniques include operational complexity, diverse stakeholder needs, evolving technology considerations, initial costs, and resistance to change.
How can retailers overcome resistance to change when adopting automation?
It is important to begin addressing potential resistance to change when adopting automation early, as part of decision-making processes. These include thorough comprehensive communication strategies, thorough training initiatives, and being sure to highlight the benefits of automation as a support – not replacement – for human roles.







