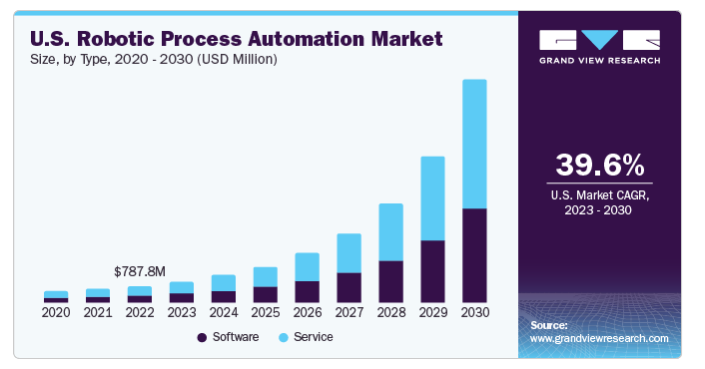
Robots are everywhere these days, revolutionizing industries far beyond factory floors, warehouses, and even home vacuum cleaners. In fact, according to a prediction by Wiss.com, 80% of all accounting tasks would be automated by 2024 and reports from Grand View Research show that the global RPA automation market is predicted to grow at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 39.9% from 2023 to 2030.
In the realm of accounting and technology, a different kind of robot is quietly reshaping operations: Robotic Process Automation (RPA). But what is this, and what does it mean?
Let's explore how RPA is reshaping the future of finance and the profound implications of RPA for businesses and financial institutions worldwide.
What Does RPA Stand For?
RPA stands for Robotic Process Automation, a form of business process technology that allows a company to configure software or an 'invisible robot' to mimic important but highly repetitive tasks that follow predefined rules. These could include capturing and interpreting data, filling in forms, moving files, and many other basic, repetitive tasks across applications.

These software bots also have the ability to execute more complex business processes, including the ability to launch and operations other software. Needless to say, any company that uses significant amounts of human laborers for these repetitive processes can both boost capability and save time and money by using RPA software.
How to Measure RPA ROI
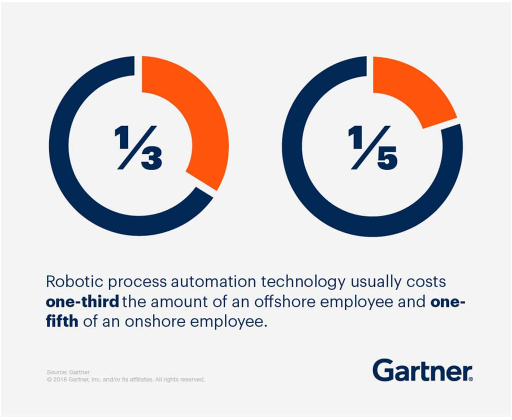
It's easy to say that using RPA software saves time and money, but how do we measure whether this is really true? The traditional approach for larger organizations involves calculating implementing RPA based on a comparative number of Full-time Equivalent (FTE) job positions. According to Gartner, one bot can take the place of up to 30x the work of a human FTE.
Note that comparing to full time positions may not be a good measurement for smaller companies. However, the fact remains that a significant amount of manual work can be done using RPA bots to reduce time and costs, increase accuracy, improve security, and enhance compliance.
For just these reasons along, these software-based bots are quickly becoming indispensable in modern accounting departments, particularly in streamlining Accounts Payable (AP) processes.
What is the Difference Between RPA and AI?
RPA has significant evolution, merging with Artificial Intelligence (AI) to enhance its capabilities. However, these terms are often combined or confused, so let's look at the differences between them.
RPA
RPA primarily focuses on automating repetitive, rule-based tasks by simulating human actions. Essentially, RPA sets the foundation for intelligent automation.

AI
AI extends beyond rule-based automation, aiming to elevate it to new heights by replicating human intelligence. It enables machines to learn from data (also known as Machine Learning or ML), adapt to new inputs, and perform tasks autonomously.
Harnessing the Power of AI, ML, and RPA
The lines between capabilities is becoming increasingly blurred, as they integrate more seamlessly to consolidate data from disparate systems, enhance automation, and foster the creation of more complex and intelligent workflows.
The Use of RPA in Finance
The integration of RPA into all finance functions represents a seismic shift rather than a passing trend. Companies are increasingly recognizing the unparalleled efficiency and accuracy that RPA brings, with previously routine manual finance tasks now seamlessly executed by intelligent programs.
In fact, the impact of RPA has been so profound as to spur the establishment of dedicated research institutions such as the Institute for Robotic Process Automation and Artificial Intelligence (IRPAAI). The entities push innovation, helping to advance the capabilities of RPA and push the boundaries of robotic process automation in finance in general.
8 Benefits of RPA for Finance and Accounting Teams
In finance departments specifically, RPA is transforming traditional financial processes. From automating data extraction, data entry, and reconciliations to facilitating compliance tasks, RPA is streamlining operations and enhancing accuracy. Here are 8 different benefits RPA provides to finance and accounting teams:
1. Efficiency Gains
By automating repetitive processes, RPA liberates employees from manual business processes and enables them to focus on other, more strategic tasks that further the organization.
2. Error Reduction
 Human errors and data discrepancies in financial transactions can have costly, time-consuming consequences. RPA eliminates the risk of human and error (and consequence) by executing tasks with both precision and consistency.
Human errors and data discrepancies in financial transactions can have costly, time-consuming consequences. RPA eliminates the risk of human and error (and consequence) by executing tasks with both precision and consistency.
This not only ensures data accuracy but also ensures compliance with regulatory standards.
3. Cost Savings
Manual processes are both time-consuming and resource intensive. By automating basic, routine tasks, an RPA implementation can significantly reduce operational costs associated with labor
4. Enhanced Compliance
Compliance regulations are constantly evolving, something that can pose a significant challenge for finance and accounting teams. RPA helps by ensuring adherence by executing tasks based on built-in rule sets and maintaining comprehensive audit trails.
This not only reduces risk but also minimizes the potential for fines and penalties.
5. Faster Insights

In today's highly competitive environment, timely access to financial insights is key to success. RPA accelerates data processing and analysis, providing finance professionals with real-time, accurate data into Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), financial trends, and other analytics.
6. Scalability and Flexibility
RPA offers easy scalability by effortlessly handling increased transaction volumes at the same quality level without the need for additional manpower. In addition, RPA bots are adaptable to changing business requirements, making them a flexible solution for any finance environment.
7. Improved Customer and Vendor Experience
By automating processes such as billing, invoicing, and payment processing, RPA ensures prompt and accurate transactions. This enhances the overall customer and vendor experience, building strong relationships and fostering long-term loyalty.
8. Employee Satisfaction and Retention
Mundane, repetitive tasks are often boring and dampen employee morale and productivity. Automating these tasks frees staff to engage in other, more stimulating work that adds value to the organization.
Fostering a culture of professional development and innovation ultimately leads to higher employee satisfaction and retention rates.
In summary, RPA offers a wide range of benefits ranging from efficiency and accuracy to compliance, cost savings, and vendor or customer satisfaction.

Common Uses of RPA in Finance
Let's explore some common uses of software robots or bots in the finance and accounting departments:
1. Invoice Processing
 No more paper! RPA streamlines the often tedious and time-consuming invoice processing tasks. Bots can extract relevant data from invoices including vendor information, invoice numbers, amounts, and more. It can then verify that data against other documentation such as Purchase Orders (POs) and delivery receipts before entering it into accounting systems. All with minimal human intervention. Once the data is retrieved and verified, RPA can forward the invoices to the predefined approvers.
No more paper! RPA streamlines the often tedious and time-consuming invoice processing tasks. Bots can extract relevant data from invoices including vendor information, invoice numbers, amounts, and more. It can then verify that data against other documentation such as Purchase Orders (POs) and delivery receipts before entering it into accounting systems. All with minimal human intervention. Once the data is retrieved and verified, RPA can forward the invoices to the predefined approvers.
This not only reduces errors and increases security, it also accelerates the entire invoice processing cycle.
2. Accounting Processes
Software bots can be programmed to performs tasks such as journal entry posting, reconciliations, and financial performance reporting. They can do them with precision and efficiency, ensuring accuracy while saving valuable manpower.
3. Financial Reporting
Generating financial reports involves gathering data from multiple sources, consolidating it, and formatting it into meaningful reports. RPA can automate this entire process, pulling data from various sources, performing calculations to analyze data, and producing customized reports according to predefined templates.
4. Expense Management 
As mentioned above, RPA can automate expense approval workflows. It can also validate expense reports and claims against company policies and even begin reimbursement processes. This streamlines the entire expense management lifecycle.
5. Compliance and Audit
Compliance with regulatory requirements and internal controls is a consistent requirement in the financial arena. RPA helps ensure compliance by carefully executing predefined audit procedures, flagging anomalies for further review, and maintaining comprehensive audit trails for documentation purposes.
6. Risk Management
Identifying and mitigating financial risk is essential for maintaining the stability, security, and credibility of an organization. RPA can play a crucial role in risk management by constantly monitoring transactions, detecting ay suspicious activities or patterns, and then triggering alerts for timely intervention by risk management professionals.
In short, RPA offers many benefits for finance departments. By leveraging RPA technology, finance teams can drive greater value for their organizations.

Ready to Free Up Time?
According to the Deloitte Global RPA Survey, the future of RPA is bright with 53% of respondents already having started their RPA journey and another 19% planning to adopt RPA in the next two years.
Per the same survey, 78% of respondents who already implemented RPA expect to significantly increase their investment over the next three years. And the results are showing. According to a study by IBM, if RPA growth trends continue, RPA will achieve "near universal adaption" within the next five years.

Don't fall behind! Reach out to Yooz today and learn more about the Yooz comprehensive, end-to-end, and AI-based automation can benefit your company.
FAQs
How does Robotic Process Automation (RPA) work in finance?
What are the benefits of implementing RPA for finance departments?
What processes can be automated using RPA?
How can RPA improve efficiency and accuracy in finance tasks such as invoice processing and reconciliation?
What are the benefits of RPA?
How can finance departments increase ROI on RPA?
Will RPA replace employees?
Can RPA be customized within our organization to fit our needs?